Upgrading Oracle DBA skills with RAC – Real Application Clusters is vital to handle critical environments where High Availability is a major requirement. We will make it easy for you to learn, implement and achieve High Availability, Load Balancing, Performance improvement in your environment with this course.
- Covers concepts and Real-Time activities.
- Install and Implement yourself.
- Simple and easy to understand.
- Align with industry standards.

Pre-requisites (Free)
No Pre-requisites needed
System Requirements
CPU: Minimum of Dual Core and Hyper threading processor
Memory: 6 GB
OS: Windows/MacOS
Space: 100 GB of disk spac
Training Details
34 Sessions.
Trainer: Pawan Kumar Yaddanapudi.
Includes supporting documents, software’s and Log files.
Anytime assistance.
Video tutorials
Learn at your own pace.
Saves 50% of your money.
Revise any number of times for 6 months.
Assured quality and content as classroom/online training.
Online training
One scheduled session per day.
Good internet connectivity required.
Batch of minimum 5 students.
Chapter 1: Introduction
- Softwares list we use
- What Is a Cluster
- What is Oracle Real Application Clusters
- Benefits of Using RAC
- Levels of Scalability
- Scaleup and Speedup
- Complete Integrated Clusterware
- Necessity of Global Resources
- Global Resources Coordination
- Global Cache cordination
- Write to Disk Coordination
- Dynamic Reconfiguration
- Dynamic Remastering
- Global Dynamic Performance Views
- Additional Memory Requirement for RAC
- Efficient Internode Row-Level Locking
- Parallel Execution with RAC
- RAC Software Principles
- RAC Software Storage Principles
- RAC Database Storage Principles
- RAC and Shared Storage Technologies
- Oracle Cluster File System
- Automatic Storage Management
- ASM Key Features and Benefits
- ASM and Grid Infrastructure in 11gR2
- CFS or Raw?
- RAC and Services
- RAC One Node Single-Instance High Availability on 11gR2.
Chapter 2: Grid Infrastructure: Overview
- Oracle Clusterware
- Oracle Clusterware Architecture and Services
- Goals for Oracle Clusterware
- Oracle Clusterware Networking
- Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a Cluster
- Grid Plug and Play
- Grid Naming Service
- Single Client Access Name
Chapter 3: Oracle RAC Installation
- Oracle RAC 11g incorporates a two-phase installation process:
- Oracle RAC 11g Installation: Outline
- Pre installation Tasks
- Network Requirements
- Virtual IP Addresses and RAC
- SCAN from 11gR2
- Install VMware and one OEL server(Node 1)
- Install OS pre-requisites
- Add ASM disks to Node 1
- Add two network adaptors
- Complete the setup on Node 1
- Clone Node 1 to Node 2
- Modify the configuration on Node 2
- Disable NTPD and test the setup(Network and ASM disks)
- Copy GRID software to Node 1 and install CLUSTER on both nodes
- Check cluster and ASM disks on both the servers
- Install database software on both the servers from Node 1
Chapter 4: SRVCTL and CRSCTL tools
- SRVCTL commands
- SRVCTL RAC administration
- CRSCTL commands
- CRSCTL RAC administration
Chapter 5: Single Instance to RAC migration
- Methods of migrating single instance database to RAC.
- Choose a single instance environment. Else create one.
- Migrate a single Instance to 2 node RAC setup.
Chapter 6: Background processes
- Background process in Cluster
- Understand Cluster resources
- Understand Cluster components
- Background Processes Specific to OracleCluster
- Oracle Clusterware Initialization
- Startup process of cluster
- Understand all background daemons of cluster
Chapter 7: RAC Database Administration
- Find the Thread numbers of instances:
- Redolog files in RAC
- Automatic Undo Management in RAC
- Start Stop RAC instances with SQLplus
- Start Stop RAC instances with SRVCTL
- Initialization parameters in RAC
- SPFILE Parameter Values and RAC
- Identical parameters between nodes
- Distinct parameters between nodes
- Quiecing RAC databases
- Terminate sessions in RAC
- SQLplus commands and Instances
Chapter 8: ASM (Automatic Storage Management)
- ASM general architecture
- ASM instance and crash recovery in RAC
- ASM initialization parameters
- ASM and SRVCTL with RAC
Chapter 9: Global Resource Management Concepts
- Need for Global Concurrency Control
- Global Resource Directory (GRD)
- Global Resource Management
- Global Resource Remastering
- Global Resource Recovery
- Global Resource Background Processes
- Global Resource Access Coordination
- Global Enqueues
- Instance Locks
- Global Cache Management: Overview
- Global Cache Management Components
- Global Cache Buffer States
- Global Cache Management Scenarios :for Single Block Reads
- Scenario 1: Read From Disk
- Scenario 2: Read-Write Cache Fusion
- Scenario 3: Write-Write Cache Fusion
- Scenario 4: Write-Read Cache Fusion
- Global Cache Management Scenarios for Multi-Block Reads
- Useful Global Resource Management Views
Chapter 10: Managing Backup and Recovery for RAC
- RAC and Instance Recovery
- Instance Recovery and Database Availability
- Instance Recovery and RAC
- Instance Recovery and RAC
- Protecting Against Media Failure
- Media Recovery in Oracle RAC
- Parallel Recovery in RAC
- Archived Log File Configurations
- RAC and the Fast Recovery Area
- Archived Redo File Conventions in RAC
- Oracle Recovery Manager
- Configuring RMAN Snapshot Control File Location
- Configuring Control File and SPFILE Autobackup
- Crosschecking on Multiple RAC Clusters Nodes
- Channel Connections to Cluster Instances
- RMAN Channel Support for the Grid
- RMAN Default Autolocation
- Distribution of Backups
- Shared Storage Backup Scheme: One Local Drive
- Shared Storage Backup Scheme: Multiple Drives
- Restoring and Recovering
Chapter 11: Administration Activities 1
- Crash Node 1/Node 2 and check the availability of database
- Setting Parallel_min_servers parameter
- Enable and disable archivelog mode in RAC
- Configure FRA to ASM disk group
- Configure FRA to generate Archive logs
- Configure proper naming convention to archive log files
- Configure proper snapshot control file location
- Configure Snapshot control file location
- Configure AUTOBACKUP SPFILE and controlfile backups
- Full database backup (No parallel slaves)
- Full database backup with parallel slaves on same node
- Full database backup with parallel slaves on other nodes(In run block)
- Full database backup with parallel slaves on same node(Configured RMAN)
- Full database backup with parallel slaves on other nodes(Configured RMAN)
- Restore and recover a lost datafile.
- Restore and recover databaseWith SPFILE
Chapter 12: Managing High Availability of Services
- Exercise demonstrating connection using service from windows
- Check the status of all listerners(scan) on all nodes
- Oracle Services
- Services for Policy- and Administrator-Managed Databases
- Default Service Connections
- Creating Services with SRVCTL
- Managing Services with srvctl
- Demonstrate how connection establishes with created service
- Using Services with Client Applications
- Services and Connection Load Balancing
- Services and Transparent Application Failover
Chapter 13: High Availability of Connections
- Client-Side Connect-Time Load Balancing
- Client-Side Connect-Time failover
- Server-Side Connect-Time Load Balancing
- Fast Application Notification: Overview
- Fast Application Notification: Benefits
- FAN-Supported Event Types
- FAN Event Status
- FAN Event Reasons
- FAN Event Format
- Connection Load Balancing in RAC
- Transparent Application Failover: Overview
- Example connection without TAF:
- TAF Basic Configuration Without FAN: Example
Chapter 14: Administration Activities 2
- Relocating services
- Starting cluster
- Bringing cluster down
- deleting services
- Modifying services
- Killing sessions
- Monitoring blocks,LOCKS, DEADLOCKS
- Starting cluster components
- View number of nodes in cluster:
- Check Cluster status:
- identify OCR
- Identify location of voting disk
- OCR backups
- adding additional voting disk
- Shutting down all oracle services for any maintenance
- Adding, Deleting, or Migrating Voting Disks
- Locating the OCR Automatic Backups
- Changing the Automatic OCR Backup Location
- Adding, Replacing, and Repairing OCR Locations
- Removing an Oracle Cluster Registry Location
- Performing Manual OCR Backups
- Recovering the OCR by Using Physical Backups
- Recovering the OCR by Using Logical Backups
- Oracle Local Registry
- Determining the Current Network Settings
- Recovering the OCR by Using Physical Backups
Chapter 15: RAC database Monitoring and Tuning
- CPU and Wait Time Tuning Dimensions
- RAC-Specific Tuning
- Analyzing Cache Fusion Impact in RAC
- Wait Events for RAC
- Wait Event Views
- Session and System Statistics
- Most Common RAC Tuning Tips
- Monitoring RAC Database and Cluster Performance
- AWR Snapshots in RAC
- Active Session History Reports for RAC
- Automatic Database Diagnostic Monitor for RAC
Chapter 16: Administration activities 3
- Adding node to the cluster
- Deleting node from the cluster
- PSU patch 11.2.0.3.8
- ASM storage administration
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Wondering what ORSKL can do for you?
Related Posts
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available but majority have suffered alteration in some.There are many variations.
- myadmin
- Data Analytics
- 1 Comments
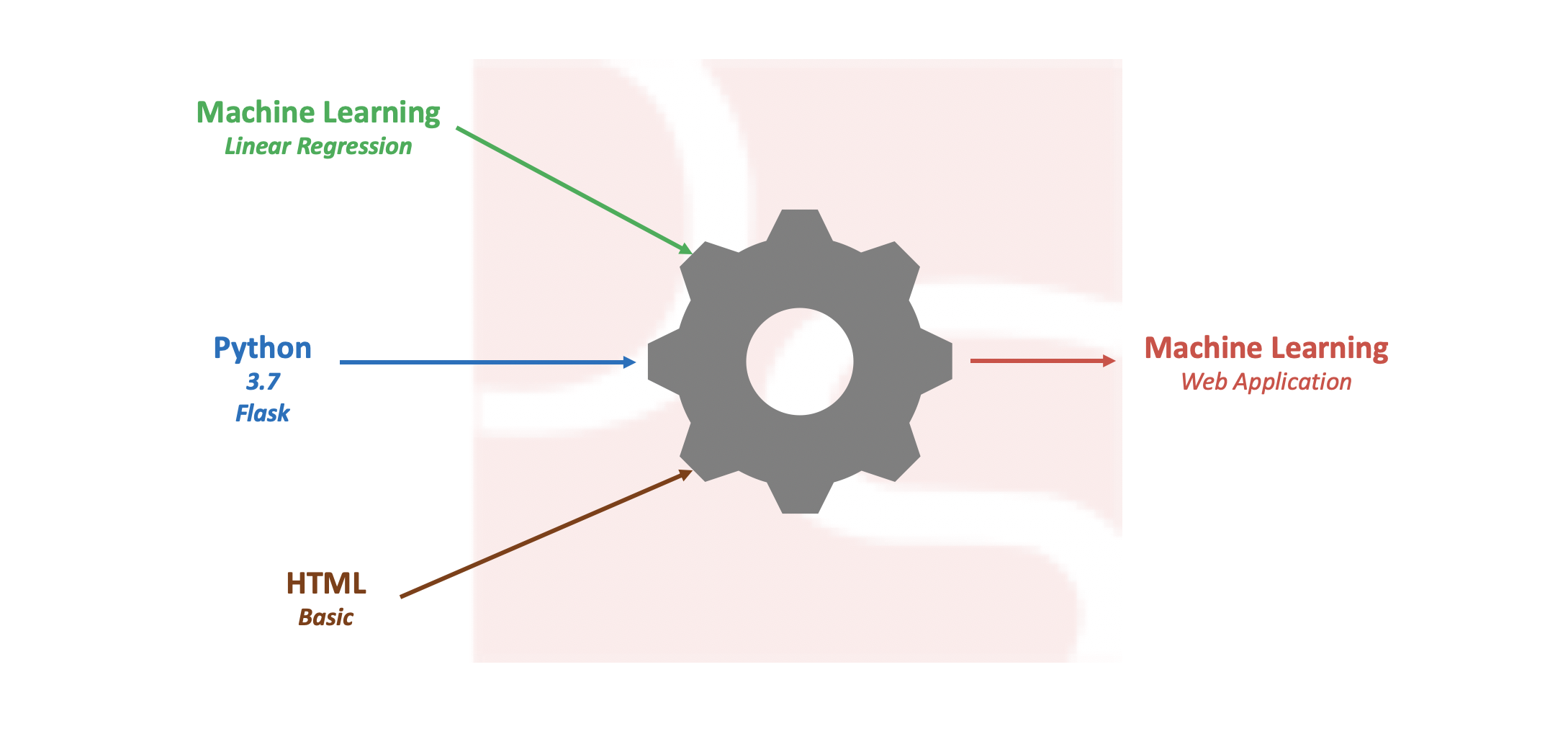
Build Simple Machine Learning Web Application using Python
Pre-processing data and developing efficient model on a given data set is one of the daily tasks of machine learning engineer with commonly used languages like Python or R. Not every machine learning engineer would get a chance or requirement to integrate the model into real time applications like web or mobile for end users […]
- myadmin
- Data Analytics
- 0 Comments
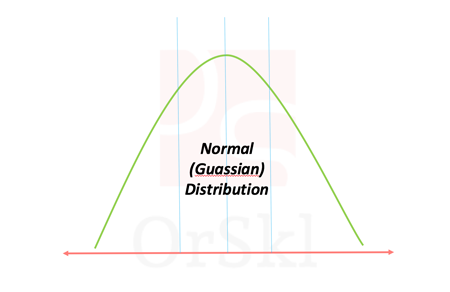
Ways to identify if data is Normally Distributed
Normal distribution also known as Gaussian distribution is one of the core probabilistic models to data scientists. Naturally occurring high volume data is approximated to follow normal distribution. According to Central limit theorem, large volume of data with multiple independent variables also assumed to follow normal distribution irrespective of their individual distributions. In reality we […]
- myadmin
- Data Analytics
- 0 Comments
Will highly correlated variables impact Linear Regression?
Linear regression is one of the basic and widely used machine learning algorithms in the area of data science and analytics for predictions. Data scientists will deal with huge dimensions of data and it will be quite challenging to build simplest linear model possible. In this process of building the model there are possibilities of […]
- myadmin
- General topics
- 14 Comments
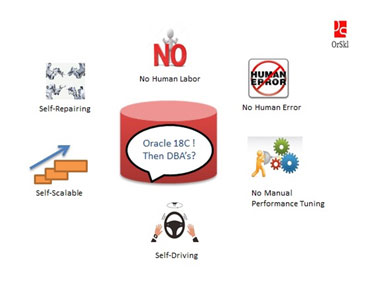
Will Oracle 18c impact DBA roles in the market?
There has been a serious concern in the market with announcement of Oracle Autonomous database 18c release. Should this be considered as a threat to Oracle DBA’s roles in the market? Let us gather facts available on the Oracle web to understand what exactly this is going to be and focus on skill improvements accordingly. […]
- myadmin
- General topics
- 4 Comments
How Oracle database does instance recovery after failures?
INSTANCE RECOVERY – Oracle database have inherit feature of recovering from instance failures automatically. SMON is the background process which plays a key role in making this possible. Though this is an automatic process that runs after the instance faces a failure, it is very important for every DBA to understand how is it made […]
- myadmin
- Performance tuning
- 16 Comments
Why should we configure limits.conf for Oracle database?
Installing Oracle Database is a very common activity to every DBA. In this process, DBA would try to configure all the pre-requisites that Oracle installation document will guide, respective to the version and OS architecture. In which the very common configuration on UNIX platforms is setting up LIMITS.CONF file from /etc/security directory. But why should […]
- myadmin
- RMAN
- 9 Comments
Why RMAN needs REDO for Database Backups?
RMAN is one of the key important utility that every Oracle DBA is dependent on for regular day to day backup and restoration activities. It is proven to be the best utility for hot backups, in-consistent backups while database is running and processing user sessions. With all that known, as an Oracle DBA it will […]
- myadmin
- General topics
- 10 Comments
Will huge Consistent Reads floods BUFFER CACHE?
Oracle Database BUFFER CACHE is one of the core important architectural memory component which holds the copies of data blocks read from datafiles. In my journey of Oracle DBA this memory component played major role in handling Performance Tuning issues. In this Blog, I will demonstrate a case study and analyze the behavior of BUFFER […]
- myadmin
- Storage
- 11 Comments
Can a data BLOCK accommodate rows of distinct tables?
In Oracle database, data BLOCK is defined as the smallest storage unit in the data files. But, there are many more concepts run around the BLOCK architecture. One of them is to understand if a BLOCK can accommodate rows from distinct tables. In this article, we are going to arrive at the justifiable answer with […]
- myadmin
- Performance tuning
- 32 Comments
Can you really flush Oracle SHARED_POOL?
One of the major player in the SGA is SHARED_POOL, without which we can say that there are no query executions. During some performance tuning trials, you would have used ALTER SYSTEM command to flush out the contents in SHARED_POOL. Do you really know what exactly this command cleans out? As we know that internally […]